Skin cancer
Skin cancer is a disease of the body's skin cells.
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the leading cause of skin cancer. While skin cancers usually appear on skin exposed to the sun, they may also appear in places that are not typically exposed to sunlight, such as between the toes, the vagina or in the mouth.There are 3 main types of skin cancer:
- basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- melanoma.
Signs and symptoms
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) are the most common form of skin cancer.
BCCs normally grow slowly and appear on the head, neck or upper body as a lump or scaling area that is red, pale or pearly in colour. They can be a spot that won't heal.
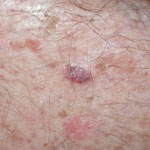
Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs)
Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs), like BCCs are a common type of skin cancer. They usually grow slowly over months and usually appear in places most often exposed to the sun. In these places they may appear as a thickened red, scaly spot that may bleed easily or ulcerate.
SCCs can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated.
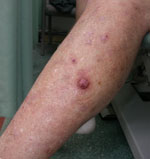
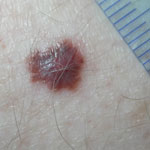
Melanomas
Melanomas are the least common type of skin cancer but are the most dangerous. They can grow quickly in weeks or slowly over months and can appear anywhere on the body appearing as a new spot or an existing spot, freckle, or a mole that changes colour, size or shape.
A melanoma can be flat or raised and is generally more than 1 colour with an irregular outline.
If left untreated, melanomas can spread to other parts of the body. If you notice a spot that you think could be a melanoma, do not delay in seeing your doctor.
Other spots
There are other types of skin spots and changes that are not skin cancer but might be a warning sign.
Dysplastic naevi appear as flat, fairly large moles anywhere on the body. They have irregular borders and uneven colour, with multiple shades of brown to pink. Dysplastic naevi indicate that a person has a higher risk of developing melanoma.
Moles can be evenly coloured, have clear edges and may be raised. They are usually circular or oval in shape.
Freckles are harmless coloured spots that range from 1 to 10 millimetres in size. However, they do indicate that the sun has damaged the skin.
Solar keratosis appear as red, flattish, scaly areas that may sting if scratched. They are a warning sign that a person has a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
Seborrhoeic keratosis have a very distinct edge and frequently sit on top of the skin. The colour varies from pale to orange and black. Their size can be from a few millimetres up to 2 centimetres.
Practical advice
- Knowing your skin and knowing what is normal for your skin is the best way to identify any changes.
- Check your skin regularly and look for any new spots or changes in the size, shape or colour of any existing moles or spots.
- Speak to your doctor about any concerns you have and ask about having a skin check.
- Always practice the 5 sun safe behaviours.


