Liver function is essential to life. The liver performs a variety of very important functions and has the ability to repair itself.
It has a considerable reserve but there are many illnesses that lead to gradual damage and deterioration of the liver’s functions. Once the deterioration has continued to the point where there is not enough healthy tissue available to support the normal bodily functions, treatment options need to be considered. Transplantation is one option that will return an improved quality of life.
Common indications for liver transplantation include:
- Cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis for example Hepatitis B or C infection
- Alcohol related liver disease
- Fatty liver disease
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Autoimmune liver diseases including autoimmune hepatitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cholangitis
- Liver failure due to severe drug reactions
- Inherited causes of liver disease and some metabolic disorders.
More information on your liver condition will be available from your treating doctor.
Liver functions
The liver has many important roles in keeping the body functioning.
- Production of bile and bile salts. These help in the digestion and absorption of fats, fat-soluble vitamins and calcium salts.
- Metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats
- Storage of glycogen, Vitamins A, D and B12, iron, lipids and cholesterol.
- Production of some blood products, albumin and clotting factors
- Metabolism or breakdown of various drugs and chemicals that would be harmful to the body.
When the liver is no longer able to complete these roles properly, we start to see complications of liver failure.
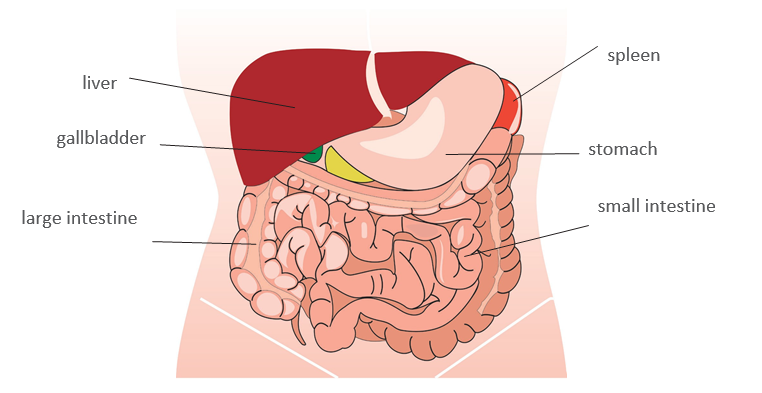
Anatomy
This diagram will assist you to have a better understanding of where the organs are located in the abdomen.