Mount Oxide remediation project
The Mount Oxide ore body was discovered by Ernest Henry in 1882. Higher-grade ore was worked by underground methods from 1927 to 1943 and again from 1955 to 1960, while the lower-grade envelope and remnants of high-grade ore were mined by open cut from 1967 to 1971.
- View a glossary of mining terms used on this page.
Underground mining produced 79,000 tonnes of ore yielding 12,500 tonnes of copper. Later mining, leaching and precipitation operations from 1962 to 1965 and 1978 to 1982 yielded an additional 1,369 tonnes of copper.
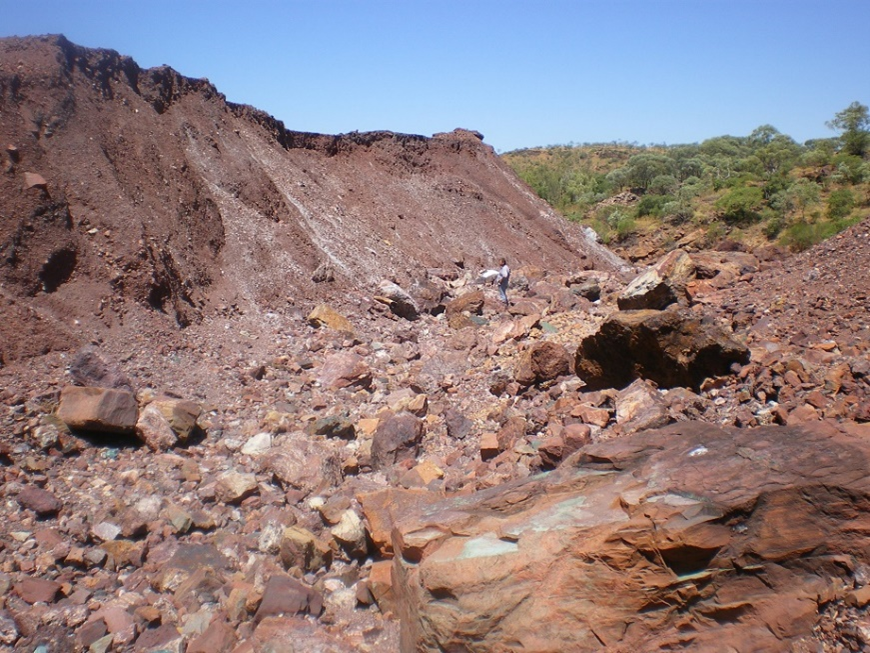
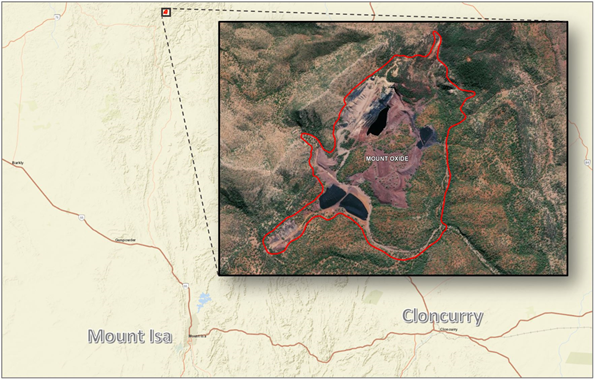
The Mount Oxide site has significant mine features including an open-cut pit, water impoundments, residual stockpiles, leach heaps and overburden dumps.
Since the cessation of leases, we have managed the site, focusing on minimising the impacts of mine-related acid and metalliferous drainage.
Project snapshot
Region: North-west Queensland
Location: 140km north of Mount Isa and 40km north-east of Mount Gordon Mine (formerly known as Gunpowder), Latitude -19.480642, Longitude 139.389725
Commodity: Copper
Mining type: Underground and open cut
Date of abandonment: August 1999
Status: Remediation ongoing
Native title interest: Kalkadoon People represented by Kalkadoon Native Tile Aboriginal Corporation RNTBC
Public land registers: Listed on the Environmental Management Register
Photo gallery
Key risks
Health and safety risks associated with high wall in open pit, waste rock stockpile and historic shaft/mine entrance.
Environmental risks associated with:
- release of acid metalliferous drainage to the downstream environment
- ingestion of mineral precipitates (salts) and mine-affected water outside stock water guidelines by livestock
- groundwater contamination.
Completed works
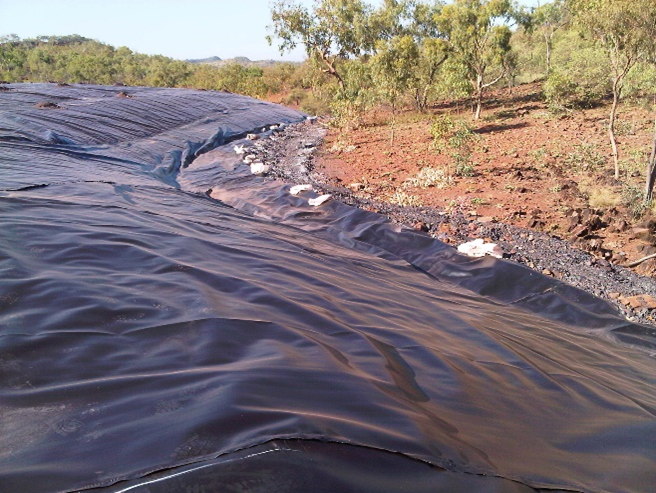
- HDPE liner installed over waste rock dumps to reduce water ingress and subsequent release of acid metalliferous drainage
- Installation of groundwater monitoring bores
- Installation of catch dams and pump-back systems to minimise acid metalliferous drainage water leaving the site
- Installation of freshwater diversion away from stockpiles to prevent freshwater interaction with potentially acid forming materials
- Major upgrades to water management infrastructure were completed in July 2021 to mitigate acid and metalliferous drainage entering downstream environment, including:
- catchment diversion drains at waste rock dump base
- freshwater diversion drain on eastern side of site
- raising existing catchment dam wall to increase capacity for retention of contaminated water
- new embankment to mitigate contaminated waters entering adjacent waterway
Planned works
- Continued water monitoring
- Telemetry upgrades